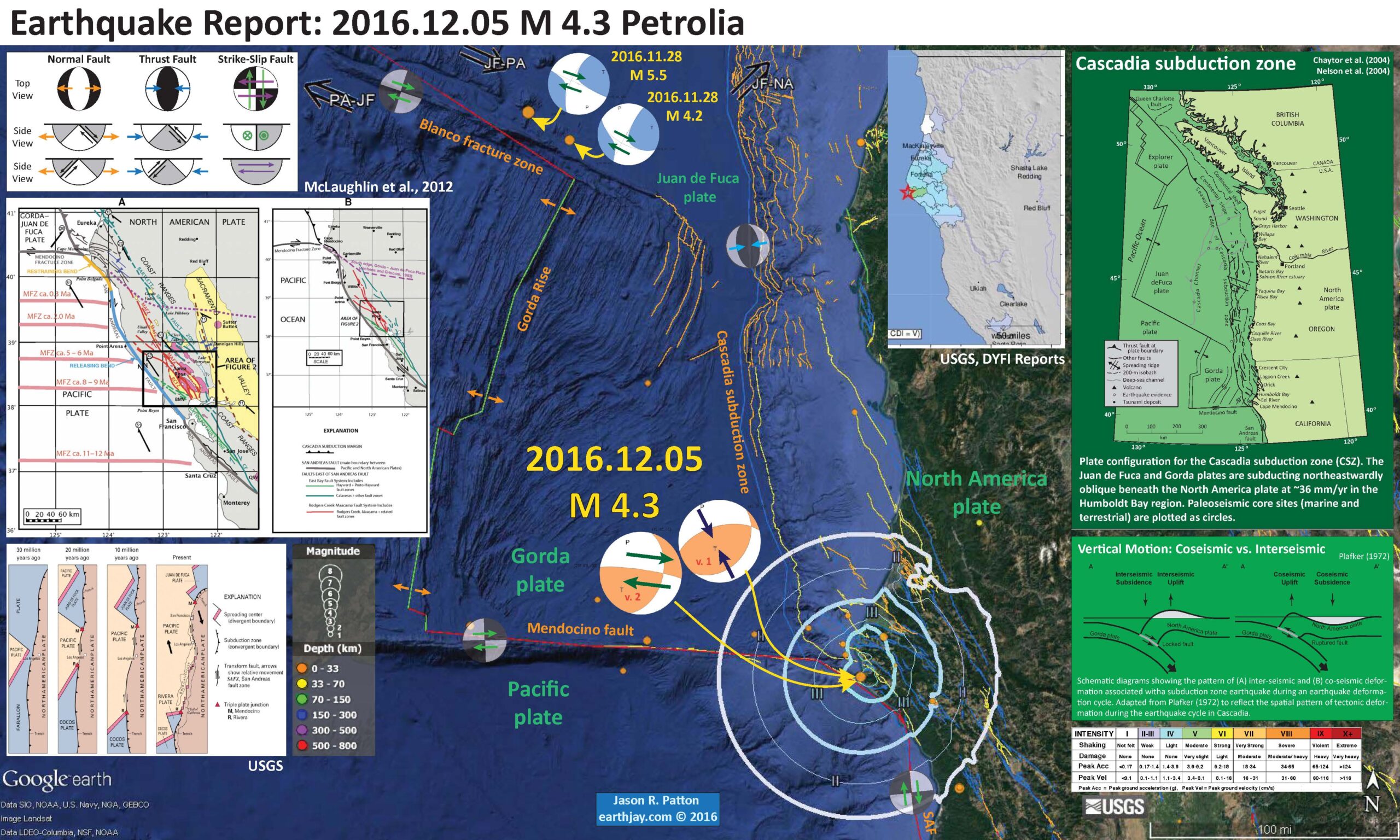
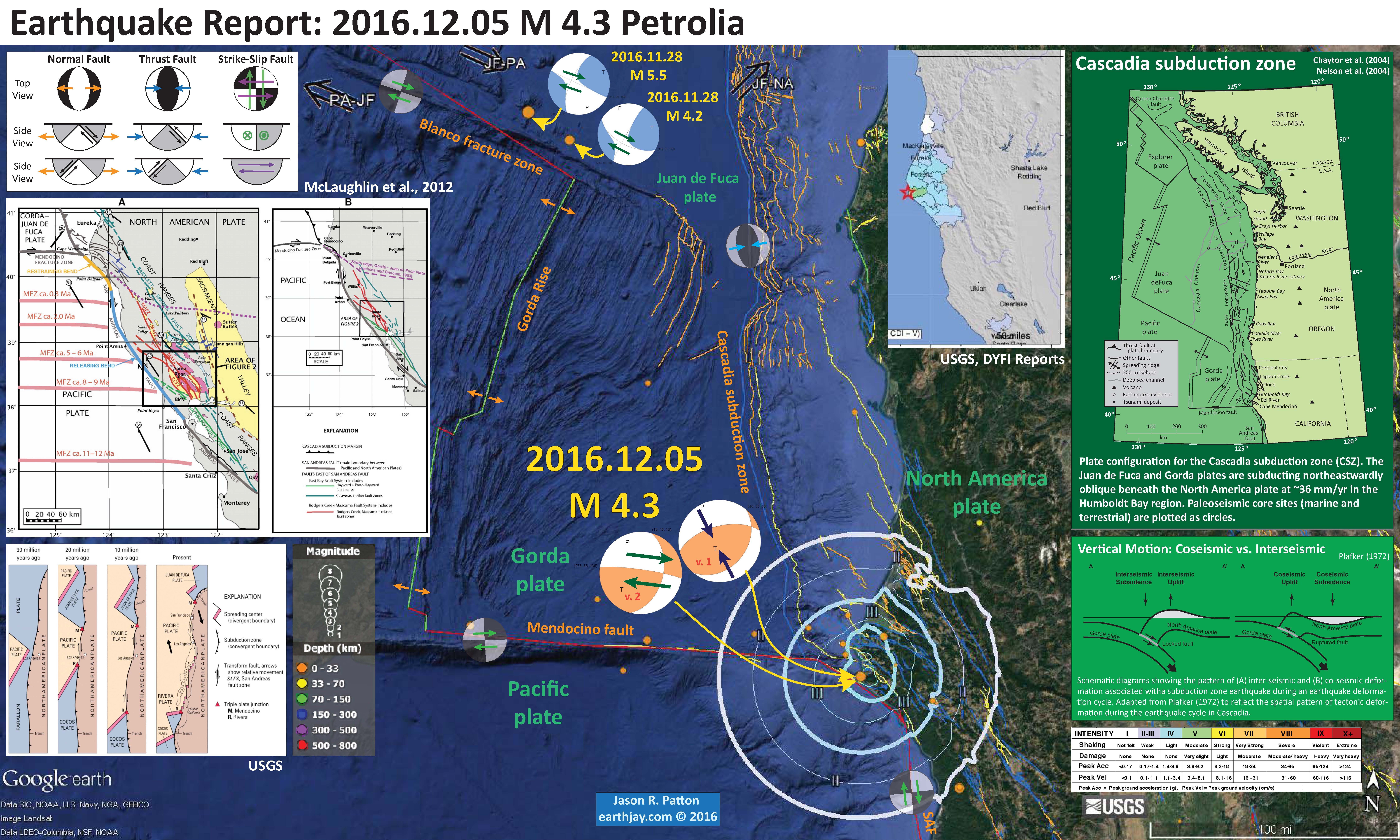
This morning there was a good shaker that was widely felt across the region. I did not feel it. I was probably driving at the time, or grading papers, which can have the same sense-deadening effect. Here is the USGS website for this M 4.3 earthquake. The earthquake occurred in an interesting part of the world, in the region of the Mendocino triple junction (MTJ) where the Cascadia subduction zone (CSZ), the San Andreas fault (SAF), and the Mendocino fault (MF) congregate. I was going to write the word “meet,” but I am not convinced that these plate boundary faults actually meet.
This earthquake appears to have occurred along the Mendocino fault, a right-lateral (dextral) transform plate boundary. This plate boundary connects the Gorda ridge and Juan de Fuca rise spreading centers with their counterparts in the Gulf of California, with the San Andreas strike-slip fault system. Transform plate boundaries are defined that they are strike-slip and that they connect spreading ridges. In this sense of the definition, the Mendocino fault and the San Andreas fault are part of the same system. This earthquake appears to have occurred in a region of the Mendocino fault that ruptured in 1994. See the figures from Rollins and Stein below. More on earthquakes in this region can be found in Earthquake Reports listed at the bottom of this page above the appendices.
The San Andreas fault is a right-lateral strike-slip transform plate boundary between the Pacific and North America plates. The plate boundary is composed of faults that are parallel to sub-parallel to the SAF and extend from the west coast of CA to the Wasatch fault (WF) system in central Utah (the WF runs through Salt Lake City and is expressed by the mountain range on the east side of the basin that Salt Lake City is built within).
The three main faults in the region north of San Francisco are the SAF, the MF, and the Bartlett Springs fault (BSF). I also place a graphical depiction of the USGS moment tensor for this earthquake. The SAF, MF, and BSF are all right lateral strike-slip fault systems. There are no active faults mapped in the region of Sunday’s epicenter, but I interpret this earthquake to have right-lateral slip. Without more seismicity or mapped faults to suggest otherwise, this is a reasonable interpretation.
The Cascadia subduction zone is a convergent plate boundary where the Juan de Fuca and Gorda plates subduct norteastwardly beneath the North America plate at rates ranging from 29- to 45-mm/yr. The Juan de Fuca and Gorda plates are formed at the Juan de Fuca Ridge and Gorda Rise spreading centers respectively. More about the CSZ can be found here.
Below I plot the seismicity from the past month, with color representing depth and diameter representing magnitude (see legend). I use the USGS Quaternary fault and fold database for the faults.
I also include the shaking intensity contours on the map. These use the Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale (MMI; see the legend on the map). This is based upon a computer model estimate of ground motions, different from the “Did You Feel It?” estimate of ground motions that is actually based on real observations. The MMI is a qualitative measure of shaking intensity. More on the MMI scale can be found here and here. This is based upon a computer model estimate of ground motions, different from the “Did You Feel It?” estimate of ground motions that is actually based on real observations.
I placed a moment tensor / focal mechanism legend on the poster. There is more material from the USGS web sites about moment tensors and focal mechanisms (the beach ball symbols). Both moment tensors and focal mechanisms are solutions to seismologic data that reveal two possible interpretations for fault orientation and sense of motion. One must use other information, like the regional tectonics, to interpret which of the two possibilities is more likely. There are two focal mechanisms for this earthquake and I include both of them on the interpretive poster below. Based on the moment tensor and my knowledge of the tectonics of this region and using the v. 2 focal mechanism, I interpret this earthquake to have had a right lateral strike slip motion along an east-west fault. However, it is equally likely that this was a northeast striking thrust fault earthquake as suggested by the v. 1 focal mechanism.
-
I have placed several inset figures.
- In the upper right corner is a map of the Cascadia subduction zone (CSZ) and regional tectonic plate boundary faults. This is modified from several sources (Chaytor et al., 2004; Nelson et al., 2004)
- Below the CSZ map is an illustration modified from Plafker (1972). This figure shows how a subduction zone deforms between (interseismic) and during (coseismic) earthquakes. Today’s earthquake did not occur along the CSZ, so did not produce crustal deformation like this. However, it is useful to know this when studying the CSZ.
- To the left of the CSZ map is the USGS Did You Feel It felt report map. This map is based upon reports submitted by real people. Note how the felt reports extend beyond the modeled estimates of MMI shaking as represented by the MMI contours on the map.
- In the lower left corner is a USGS figure that shows the evolution of these plate boundary systems.
- Above the USGS figure is a map that shows more details about the evolution of the MTJ region for the last 12 Ma (million years). This is from a paper by McLaughlin et al. (2012).
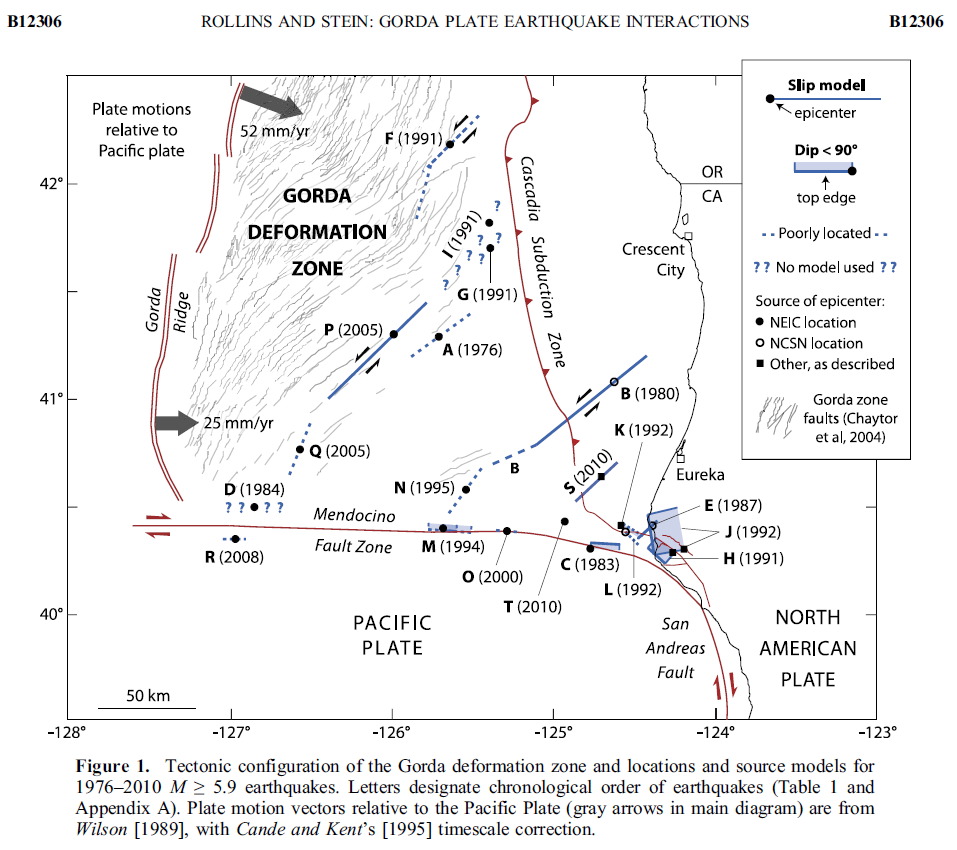
- Here is a map from Rollins and Stein, showing their interpretations of different historic earthquakes in the region. This was published in response to the January 2010 Gorda plate earthquake. The faults are from Chaytor et al. (2004). The 1980, 1992, 1994, 2005, and 2010 earthquakes are plotted and labeled. I did not mention the 2010 earthquake, but it most likely was just like 1980 and 2005, a left-lateral strike-slip earthquake on a northeast striking fault.
- Here is a large scale map of the 1983 earthquake swarm. The mainshock epicenter is a black star and epicenters are denoted as white circles. Note how the aftershocks trend slightly southeast in this region. Today’s swarm does the same (and the moment tensor also shows a slightly southeast strike). Note how the interpreted fault dips slightly to the north, which is the result of north-south compression from the relative northward motion of the Pacific plate.
- Here is a large scale map of the 1994 earthquake swarm. The mainshock epicenter is a black star and epicenters are denoted as white circles.
- Here is a plot of focal mechanisms from the Dengler et al. (1995) paper in California Geology.
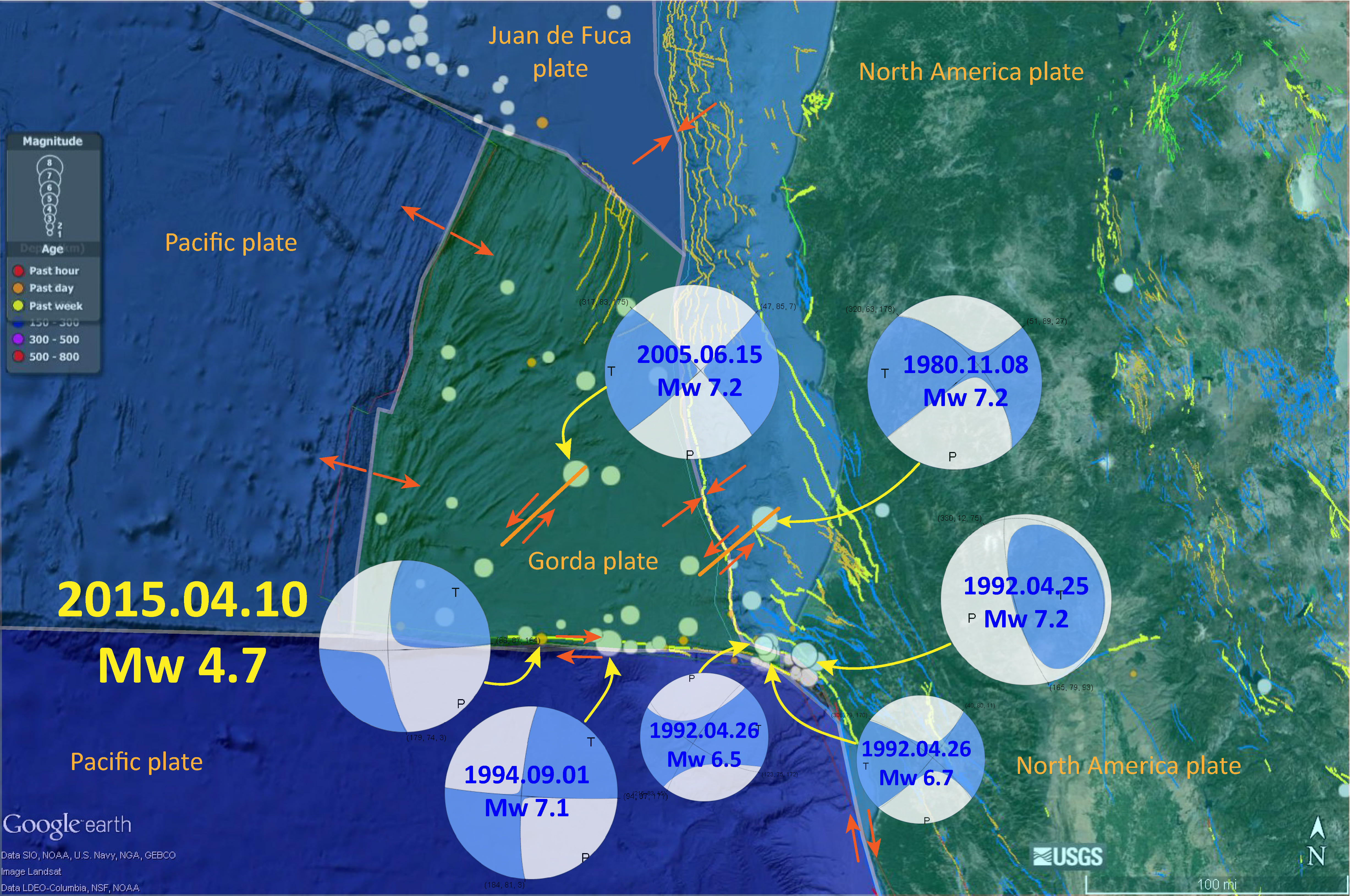
- In this map below, I label a number of other significant earthquakes in this Mendocino triple junction region. Another historic right-lateral earthquake on the Mendocino fault system was in 1994. There was a series of earthquakes possibly along the easternmost section of the Mendocino fault system in late January 2015, here is my post about that earthquake series.
- The Gorda and Juan de Fuca plates subduct beneath the North America plate to form the Cascadia subduction zone fault system. In 1992 there was a swarm of earthquakes with the magnitude Mw 7.2 Mainshock on 4/25. Initially this earthquake was interpreted to have been on the Cascadia subduction zone (CSZ). The moment tensor shows a compressional mechanism. However the two largest aftershocks on 4/26/1992 (Mw 6.5 and Mw 6.7), had strike-slip moment tensors. These two aftershocks align on what may be the eastern extension of the Mendocino fault.
- There have been several series of intra-plate earthquakes in the Gorda plate. Two main shocks that I plot of this type of earthquake are the 1980 (Mw 7.2) and 2005 (Mw 7.2) earthquakes. I place orange lines approximately where the faults are that ruptured in 1980 and 2005. These are also plotted in the Rollins and Stein (2010) figure above. The Gorda plate is being deformed due to compression between the Pacific plate to the south and the Juan de Fuca plate to the north. Due to this north-south compression, the plate is deforming internally so that normal faults that formed at the spreading center (the Gorda Rise) are reactivated as left-lateral strike-slip faults. In 2014, there was another swarm of left-lateral earthquakes in the Gorda plate. I posted some material about the Gorda plate setting on this page.
- There are three types of earthquakes, strike-slip, compressional (reverse or thrust, depending upon the dip of the fault), and extensional (normal). Here is are some animations of these three types of earthquake faults. Many of the earthquakes people are familiar with in the Mendocino triple junction region are either compressional or strike slip. The following three animations are from IRIS.
Strike Slip:
Compressional:
Extensional:
- This figure shows what a transform plate boundary fault is. Looking down from outer space, the crust on either side of the fault moves side-by-side. When one is standing on the ground, on one side of the fault, looking across the fault as it moves… If the crust on the other side of the fault moves to the right, the fault is a “right lateral” strike slip fault. The Mendocino and San Andreas faults are right-lateral (dextral) strike-slip faults. I believe this is from Pearson Higher Ed.
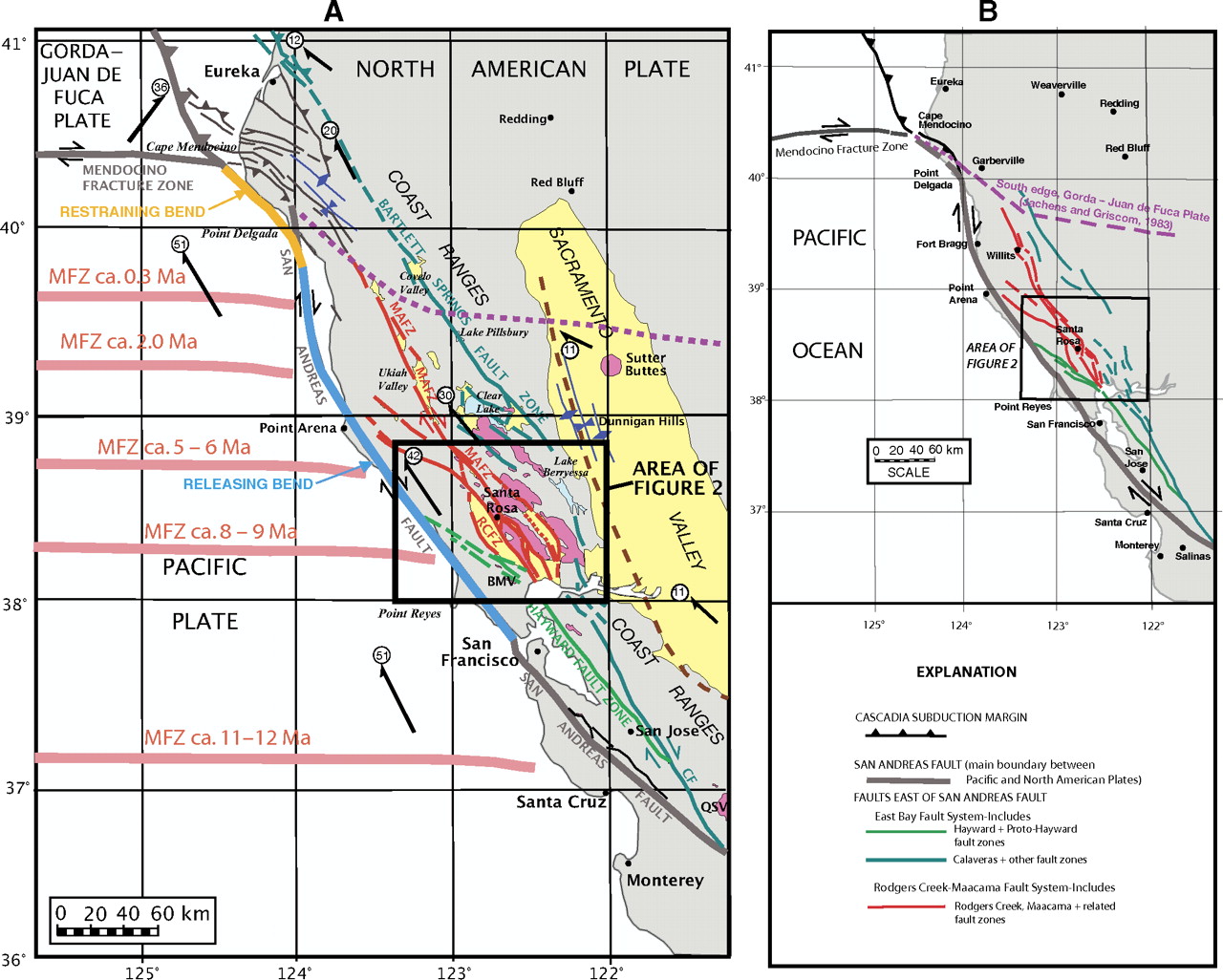
- Here is a map from McLaughlin et al. (2012) that shows the regional faulting. I include the figure caption as a blockquote below.
Maps showing the regional setting of the Rodgers Creek–Maacama fault system and the San Andreas fault in northern California. (A) The Maacama (MAFZ) and Rodgers Creek (RCFZ) fault zones and related faults (dark red) are compared to the San Andreas fault, former and present positions of the Mendocino Fracture Zone (MFZ; light red, offshore), and other structural features of northern California. Other faults east of the San Andreas fault that are part of the wide transform margin are collectively referred to as the East Bay fault system and include the Hayward and proto-Hayward fault zones (green) and the Calaveras (CF), Bartlett Springs, and several other faults (teal). Fold axes (dark blue) delineate features associated with compression along the northern and eastern sides of the Coast Ranges. Dashed brown line marks inferred location of the buried tip of an east-directed tectonic wedge system along the boundary between the Coast Ranges and Great Valley (Wentworth et al., 1984; Wentworth and Zoback, 1990). Dotted purple line shows the underthrust south edge of the Gorda–Juan de Fuca plate, based on gravity and aeromagnetic data (Jachens and Griscom, 1983). Late Cenozoic volcanic rocks are shown in pink; structural basins associated with strike-slip faulting and Sacramento Valley are shown in yellow. Motions of major fault blocks and plates relative to fi xed North America, from global positioning system and paleomagnetic studies (Argus and Gordon, 2001; Wells and Simpson, 2001; U.S. Geological Survey, 2010), shown with thick black arrows; circled numbers denote rate (in mm/yr). Restraining bend segment of the northern San Andreas fault is shown in orange; releasing bend segment is in light blue. Additional abbreviations: BMV—Burdell Mountain Volcanics; QSV—Quien Sabe Volcanics. (B) Simplifi ed map of color-coded faults in A, delineating the principal fault systems and zones referred to in this paper.
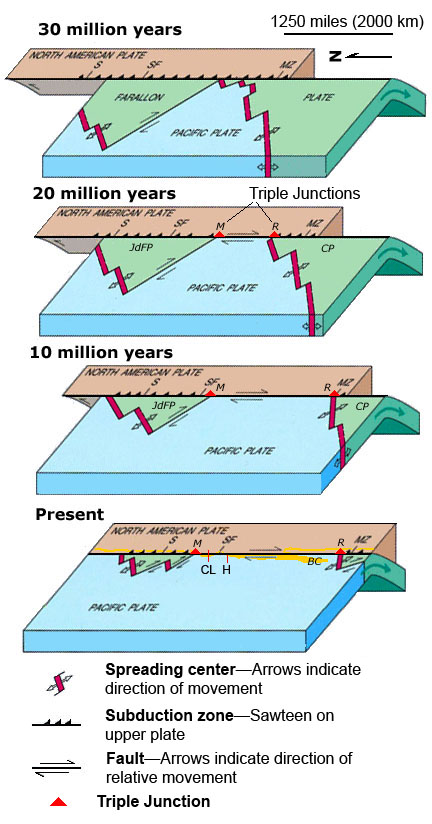
- Here is the figure showing the evolution of the SAF since its inception about 29 Ma. I include the USGS figure caption below as a blockquote.
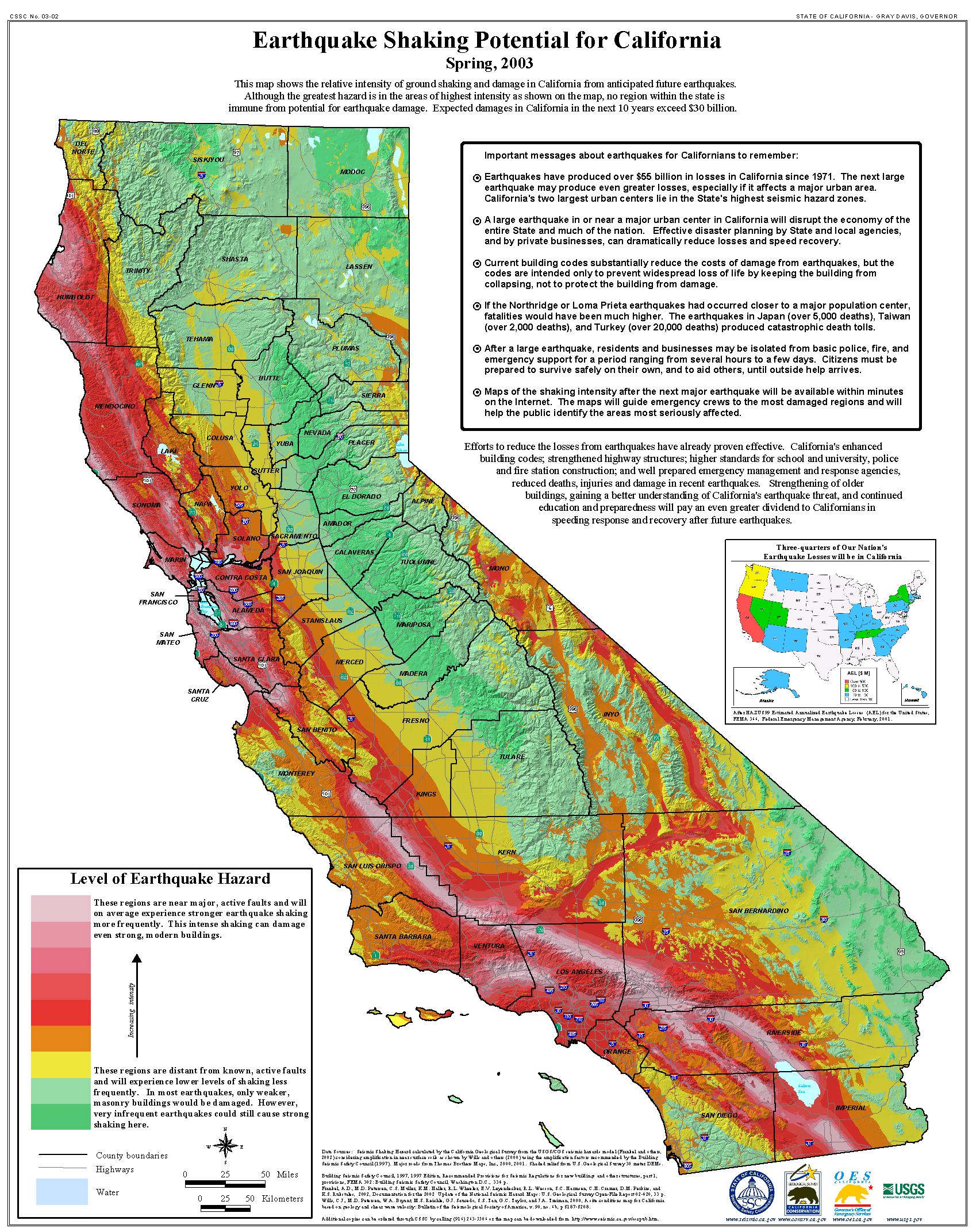
- Here is a map that shows the shaking potential for earthquakes in CA. This comes from the state of California here.
- Cascadia’s 315th Anniversary 2015.01.26
- Earthquake Information about the CSZ 2015.10.08
- 2016.09.25 M 5.0 Gorda plate
- 2016.09.25 M 5.0 Gorda plate
- 2016.07.21 M 4.7 Gorda plate p-1
- 2016.07.21 M 4.7 Gorda plate p-2
- 2016.01.30 M 5.0 Gorda plate
- 2015.12.29 M 4.9 Gorda plate
- 2015.11.18 M 3.2 Gorda plate
- 2014.03.13 M 5.2 Gorda Rise
- 2014.03.09 M 6.8 Gorda plate p-1
- 2014.03.23 M 6.8 Gorda plate p-2
- 2015.06.01 M 5.8 Blanco fracture zone p-1
- 2015.06.01 M 5.8 Blanco fracture zone p-2 (animations)
- 2016.10.27 M 4.1 Mendocino fault
- 2016.09.03 M 5.6 Mendocino
- 2016.01.02 M 4.5 Mendocino fault
- 2015.11.01 M 4.3 Mendocino fault
- 2015.01.28 M 5.7 Mendocino fault
- 2016.11.02 M 3.6 Oregon
- 2016.01.07 M 4.2 NAP(?)
- 2015.10.29 M 3.4 Bayside
- 2016.03.19 M 5.2 Explorer plate
- 2016.11.06 M 4.1 Laytonville, CA
- 2016.11.03 M 3.8 Laytonville, CA
- 2016.08.10 M 5.1 Lake Pillsbury, CA
- 2015.08.30 M 3.6 Mendocino County, CA
- 2015.07.27 M 3.5 Point Arena, CA
- 2016.02.23 M 4.9 Bakersfield
- 2015.12.30 M 4.4 San Bernardino, CA
- 2015.05.03 M 3.8 Los Angeles, CA
- 2015.04.13 M 3.3 Los Angeles, CA
- 2014.04.01 M 5.1 La Habra p-3
- 2014.03.29 M 5.1 La Habra p-2
- 2014.03.28 M 5.1 La Habra p-1
- 2016.08.04 M 4.5 Honey Lake, CA
- Geist, E.L. and Andrews D.J., 2000. Slip rates on San Francisco Bay area faults from anelastic deformation of the continental lithosphere, Journal of Geophysical Research, v. 105, no. B11, p. 25,543-25,552.
- Irwin, W.P., 1990. Quaternary deformation, in Wallace, R.E. (ed.), 1990, The San Andreas Fault system, California: U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1515, online at: http://pubs.usgs.gov/pp/1990/1515/
- McLaughlin, R.J., Sarna-Wojcicki, A.M., Wagner, D.L., Fleck, R.J., Langenheim, V.E., Jachens, R.C., Clahan, K., and Allen, J.R., 2012. Evolution of the Rodgers Creek–Maacama right-lateral fault system and associated basins east of the northward-migrating Mendocino Triple Junction, northern California in Geosphere, v. 8, no. 2., p. 342-373.
- Stoffer, P.W., 2006, Where’s the San Andreas Fault? A guidebook to tracing the fault on public lands in the San Francisco Bay region: U.S. Geological Survey General Interest Publication 16, 123 p., online at http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/2006/16/
- Wallace, Robert E., ed., 1990, The San Andreas fault system, California: U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1515, 283 p. [http://pubs.usgs.gov/pp/1988/1434/].
EVOLUTION OF THE SAN ANDREAS FAULT.
This series of block diagrams shows how the subduction zone along the west coast of North America transformed into the San Andreas Fault from 30 million years ago to the present. Starting at 30 million years ago, the westward- moving North American Plate began to override the spreading ridge between the Farallon Plate and the Pacific Plate. This action divided the Farallon Plate into two smaller plates, the northern Juan de Fuca Plate (JdFP) and the southern Cocos Plate (CP). By 20 million years ago, two triple junctions began to migrate north and south along the western margin of the West Coast. (Triple junctions are intersections between three tectonic plates; shown as red triangles in the diagrams.) The change in plate configuration as the North American Plate began to encounter the Pacific Plate resulted in the formation of the San Andreas Fault. The northern Mendicino Triple Junction (M) migrated through the San Francisco Bay region roughly 12 to 5 million years ago and is presently located off the coast of northern California, roughly midway between San Francisco (SF) and Seattle (S). The Mendicino Triple Junction represents the intersection of the North American, Pacific, and Juan de Fuca Plates. The southern Rivera Triple Junction (R) is presently located in the Pacific Ocean between Baja California (BC) and Manzanillo, Mexico (MZ). Evidence of the migration of the Mendicino Triple Junction northward through the San Francisco Bay region is preserved as a series of volcanic centers that grow progressively younger toward the north. Volcanic rocks in the Hollister region are roughly 12 million years old whereas the volcanic rocks in the Sonoma-Clear Lake region north of San Francisco Bay range from only few million to as little as 10,000 years old. Both of these volcanic areas and older volcanic rocks in the region are offset by the modern regional fault system. (Image modified after original illustration by Irwin, 1990 and Stoffer, 2006.)
Earthquake shaking hazards are calculated by projecting earthquake rates based on earthquake history and fault slip rates, the same data used for calculating earthquake probabilities. New fault parameters have been developed for these calculations and are included in the report of the Working Group on California Earthquake Probabilities. Calculations of earthquake shaking hazard for California are part of a cooperative project between USGS and CGS, and are part of the National Seismic Hazard Maps. CGS Map Sheet 48 (revised 2008) shows potential seismic shaking based on National Seismic Hazard Map calculations plus amplification of seismic shaking due to the near surface soils.
1 thought on “Earthquake Report: Petrolia (CA)”