Good Morning Humboldt County!
I was in bed checking up on social media stuff and I checked my email. There were two emails from USGS ENS showing a M 5.0 near me. I had not felt it and when I went to the USGS websites, the event had been deleted. However, when i returned to twitter, I noticed @Allomax had tweeted about a M 5.7 on the Mendocino fault. So, I got out of bed and made some coffee (half decaf). It has been a busy January (lots of earthquakes).
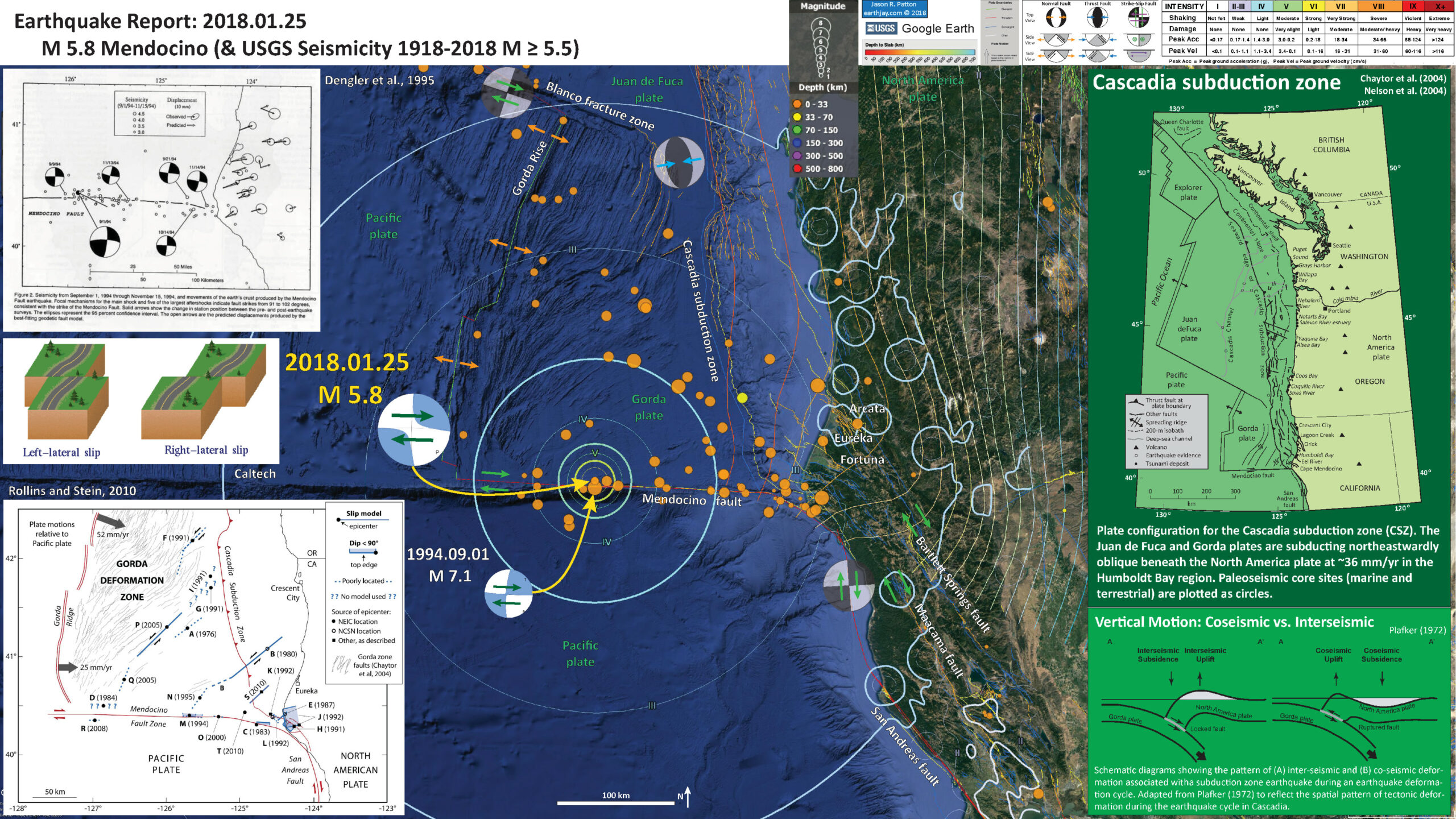
Today’s M 5.8 earthquake happened along the Mendocino fault zone, very close to the 1994 M 7.1 epicenter. Given this being an offshore location, the location uncertainty with those settings, these may have both happened in the same location.
Today’s M 5.8 earthquake was along the western part of the Mendocino fault (MF), a right-lateral (dextral) transform plate boundary. This plate boundary connects the Gorda ridge and Juan de Fuca rise spreading centers with their counterparts in the Gulf of California, with the San Andreas strike-slip fault system. Transform plate boundaries are defined that they are strike-slip and that they connect spreading ridges. In this sense of the definition, the Mendocino fault and the San Andreas fault are part of the same system. Here is the USGS website for this earthquake.
See the figures from Rollins and Stein (2010) below. More on earthquakes in this region can be found in Earthquake Reports listed at the bottom of this page above the appendices.
The San Andreas fault is a right-lateral strike-slip transform plate boundary between the Pacific and North America plates. The plate boundary is composed of faults that are parallel to sub-parallel to the SAF and extend from the west coast of CA to the Wasatch fault (WF) system in central Utah (the WF runs through Salt Lake City and is expressed by the mountain range on the east side of the basin that Salt Lake City is built within).
The three main faults in the region north of San Francisco are the SAF, the MF, and the Bartlett Springs fault (BSF). I also place a graphical depiction of the USGS moment tensor for this fault. The SAF, MF, and BSF are all right lateral strike-slip fault systems. There are no active faults mapped in the region of Sunday’s epicenter, but I interpret this earthquake to have right-lateral slip. Without more seismicity or mapped faults to suggest otherwise, this is a reasonable interpretation.
The Cascadia subduction zone is a convergent plate boundary where the Juan de Fuca and Gorda plates (JDFP and GP, respectively) subduct norteastwardly beneath the North America plate at rates ranging from 29- to 45-mm/yr. The Juan de Fuca and Gorda plates are formed at the Juan de Fuca Ridge and Gorda Rise spreading centers respectively. More about the CSZ can be found here.
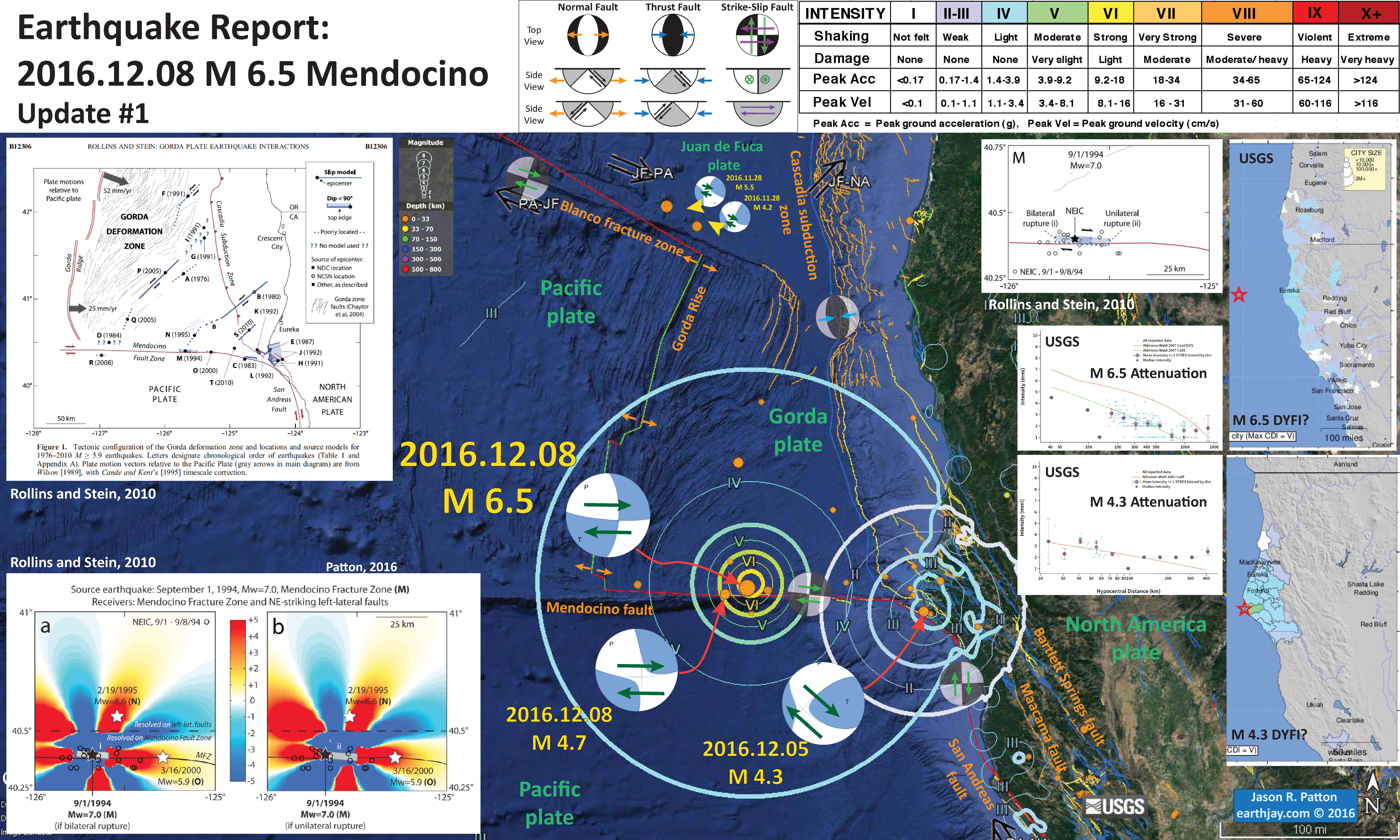
There was a good sized (M 6.5) MF earthquake late in 2016 2016.12.08. I present my poster for that earthquake below. Here is my report for that earthquake. Here is the updated report.
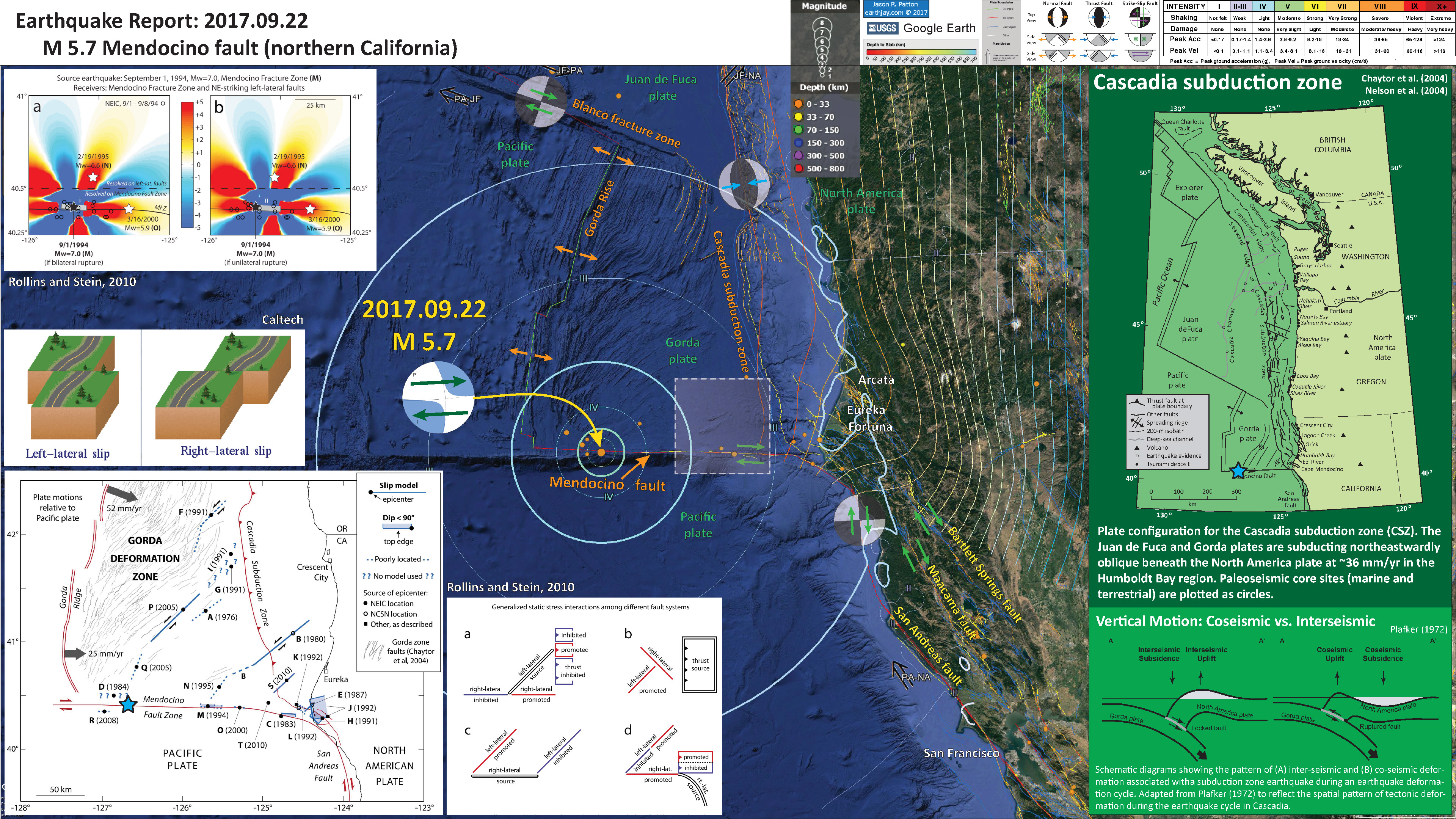
There was also a M 5.7 earthquake in 2017 (2017.09.22). Here is my report for that earthquake.
Below is my interpretive poster for this earthquake
I plot the seismicity from the past month, with color representing depth and diameter representing magnitude (see legend). I include earthquake epicenters from 1918-2018 with magnitudes M ≥ 5.5.
I plot the USGS fault plane solutions (moment tensors in blue and focal mechanisms in orange) for the M 5.8 earthquake, in addition to the 1994 Mendocino fault earthquake.
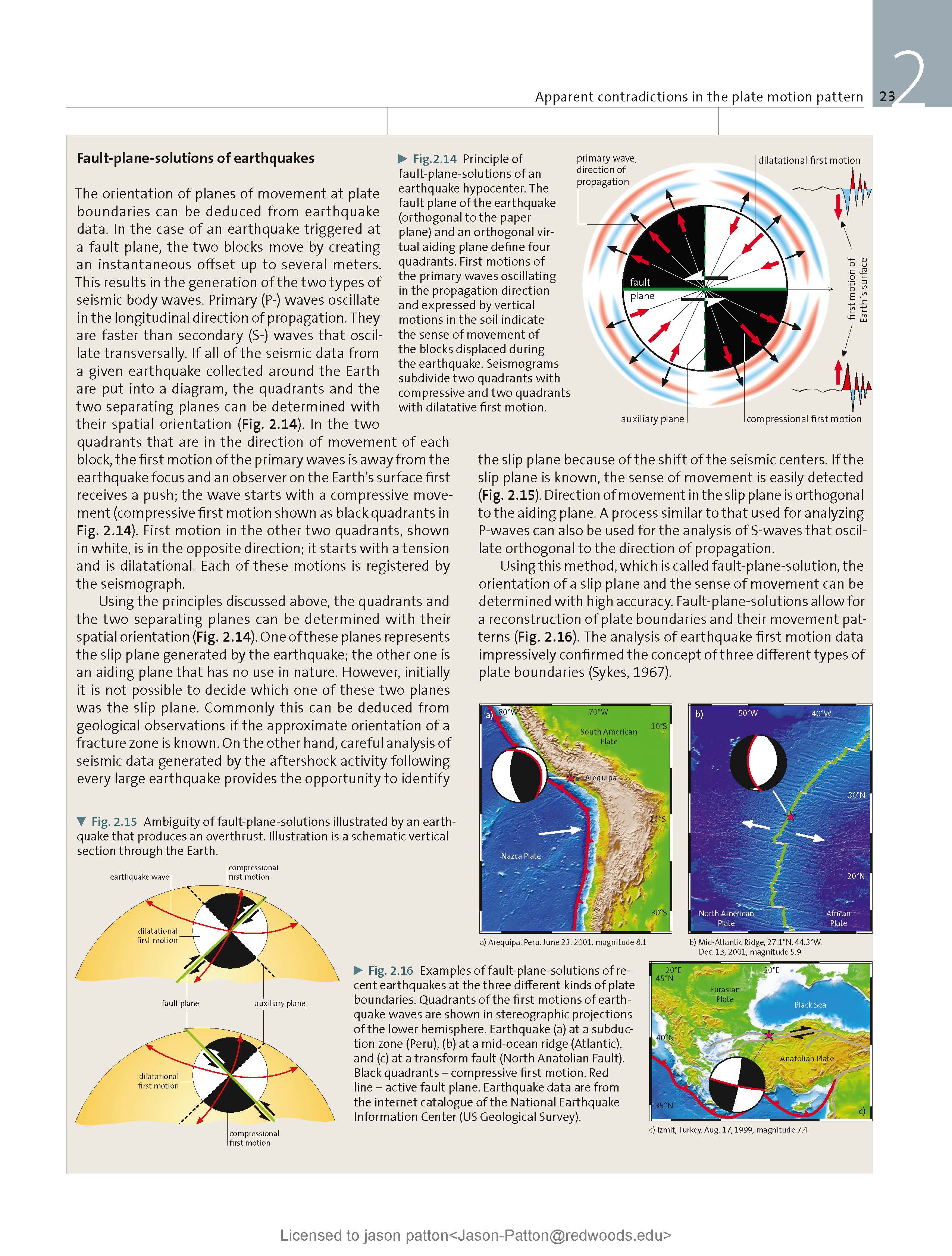
- I placed a moment tensor / focal mechanism legend on the poster. There is more material from the USGS web sites about moment tensors and focal mechanisms (the beach ball symbols). Both moment tensors and focal mechanisms are solutions to seismologic data that reveal two possible interpretations for fault orientation and sense of motion. One must use other information, like the regional tectonics, to interpret which of the two possibilities is more likely.
- I also include the shaking intensity contours on the map. These use the Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale (MMI; see the legend on the map). This is based upon a computer model estimate of ground motions, different from the “Did You Feel It?” estimate of ground motions that is actually based on real observations. The MMI is a qualitative measure of shaking intensity. More on the MMI scale can be found here and here. This is based upon a computer model estimate of ground motions, different from the “Did You Feel It?” estimate of ground motions that is actually based on real observations.
- I include the slab contours plotted (Hayes et al., 2012), which are contours that represent the depth to the subduction zone fault. These are mostly based upon seismicity. The depths of the earthquakes have considerable error and do not all occur along the subduction zone faults, so these slab contours are simply the best estimate for the location of the fault.
-
I include some inset figures.
- In the upper right corner is a map of the Cascadia subduction zone (CSZ) and regional tectonic plate boundary faults. This is modified from several sources (Chaytor et al., 2004; Nelson et al., 2004). I placed a blue star in the general location of today’s M 5.7 earthquake.
- Below the CSZ map is an illustration modified from Plafker (1972). This figure shows how a subduction zone deforms between (interseismic) and during (coseismic) earthquakes. Today’s earthquake did not occur along the CSZ, so did not produce crustal deformation like this. However, it is useful to know this when studying the CSZ.
- In the lower left corner is a figure from Rollins and Stein (2010). In their paper they discuss how static coulomb stress changes from earthquakes may impart (or remove) stress from adjacent crust/faults. This map shows the major earthquakes that have occurred in this region, prior to their publication in 2010. I place a blue star in the general location of today’s earthquake.
- In the upper left corner is a map showing historic focal mechanisms along the MF (Dengler et al., 1995). This figure shows how the GPS sites moved during that earthquake, showing that the CSZ megathrust fault is seismologically coupled.
- Here is a photo from the Humboldt State University, Department of Geology, Baby Benioff. Photo credit: Dr. Mark Hemphill-Haley.
- Below is the video provided by Mike Dronkers at Humboldt State University. This video was tweeted earlier today (see tweet in Social Media section below). Thanks Mike for sharing this video!
- Here is the poster from the 2016 M 6.5 earthquake.
- Here is the poster from the 2017 M 5.7 earthquake.
Some Relevant Discussion and Figures
- Here is a map from Rollins and Stein, showing their interpretations of different historic earthquakes in the region. This was published in response to the January 2010 Gorda plate earthquake. The faults are from Chaytor et al. (2004). The 1980, 1992, 1994, 2005, and 2010 earthquakes are plotted and labeled. I did not mention the 2010 earthquake, but it most likely was just like 1980 and 2005, a left-lateral strike-slip earthquake on a northeast striking fault.
Tectonic configuration of the Gorda deformation zone and locations and source models for 1976–2010 M ≥ 5.9 earthquakes. Letters designate chronological order of earthquakes (Table 1 and Appendix A). Plate motion vectors relative to the Pacific Plate (gray arrows in main diagram) are from Wilson [1989], with Cande and Kent’s [1995] timescale correction.
- Here is the Rollins and Stein (2010) figure that is in the report above. I include their figure caption as blockquote below.
Coulomb stress changes imparted by our models of (a) a bilateral rupture and (b) a unilateral eastward rupture for the 1994 Mw = 7.0 Mendocino Fault Zone earthquake to the epicenters of the 1995 Mw = 6.6 southern Gorda zone earthquake (N) and the 2000 Mw = 5.9 Mendocino Fault Zone earthquake (O). Calculation depth is 5 km.
- Here is a large scale map of the 1994 earthquake swarm. The mainshock epicenter is a black star and epicenters are denoted as white circles.
- Here is a plot of focal mechanisms from the Dengler et al. (1995) paper in California Geology.
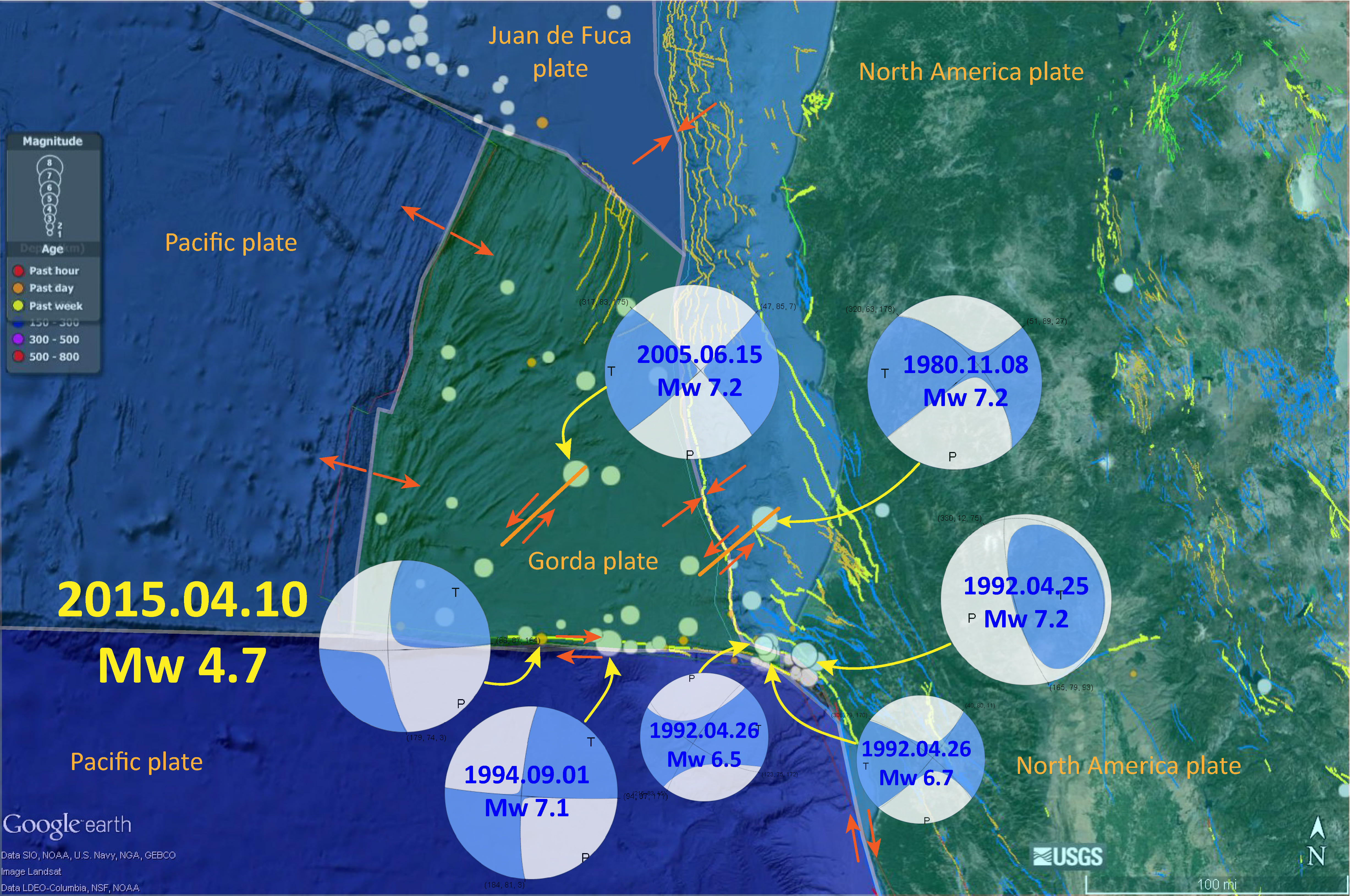
- In this map below, I label a number of other significant earthquakes in this Mendocino triple junction region. Another historic right-lateral earthquake on the Mendocino fault system was in 1994. There was a series of earthquakes possibly along the easternmost section of the Mendocino fault system in late January 2015, here is my post about that earthquake series.
- For more on the graphical representation of moment tensors and focal mechnisms, check this IRIS video out:
- Here is a fantastic infographic from Frisch et al. (2011). This figure shows some examples of earthquakes in different plate tectonic settings, and what their fault plane solutions are. There is a cross section showing these focal mechanisms for a thrust or reverse earthquake. The upper right corner includes my favorite figure of all time. This shows the first motion (up or down) for each of the four quadrants. This figure also shows how the amplitude of the seismic waves are greatest (generally) in the middle of the quadrant and decrease to zero at the nodal planes (the boundary of each quadrant).
- The Gorda and Juan de Fuca plates subduct beneath the North America plate to form the Cascadia subduction zone fault system. In 1992 there was a swarm of earthquakes with the magnitude Mw 7.2 Mainshock on 4/25. Initially this earthquake was interpreted to have been on the Cascadia subduction zone (CSZ). The moment tensor shows a compressional mechanism. However the two largest aftershocks on 4/26/1992 (Mw 6.5 and Mw 6.7), had strike-slip moment tensors. These two aftershocks align on what may be the eastern extension of the Mendocino fault.
- There have been several series of intra-plate earthquakes in the Gorda plate. Two main shocks that I plot of this type of earthquake are the 1980 (Mw 7.2) and 2005 (Mw 7.2) earthquakes. I place orange lines approximately where the faults are that ruptured in 1980 and 2005. These are also plotted in the Rollins and Stein (2010) figure above. The Gorda plate is being deformed due to compression between the Pacific plate to the south and the Juan de Fuca plate to the north. Due to this north-south compression, the plate is deforming internally so that normal faults that formed at the spreading center (the Gorda Rise) are reactivated as left-lateral strike-slip faults. In 2014, there was another swarm of left-lateral earthquakes in the Gorda plate. I posted some material about the Gorda plate setting on this page.
- There are three types of earthquakes, strike-slip, compressional (reverse or thrust, depending upon the dip of the fault), and extensional (normal). Here is are some animations of these three types of earthquake faults. Many of the earthquakes people are familiar with in the Mendocino triple junction region are either compressional or strike slip. The following three animations are from IRIS.
Strike Slip:
Compressional:
Extensional:
- This figure shows what a transform plate boundary fault is. Looking down from outer space, the crust on either side of the fault moves side-by-side. When one is standing on the ground, on one side of the fault, looking across the fault as it moves… If the crust on the other side of the fault moves to the right, the fault is a “right lateral” strike slip fault. The Mendocino and San Andreas faults are right-lateral (dextral) strike-slip faults. I believe this is from Pearson Higher Ed.
Social Media
Mw=5.9, OFF COAST OF NORTHERN CALIFORNIA (Depth: 8 km), 2018/01/25 16:39:43 UTC – Full details here: https://t.co/P2JUNvWnMU pic.twitter.com/gv0plsffwr
— Earthquakes (@geoscope_ipgp) January 25, 2018
M5.8 #earthquake Off Coast of Northern California:
Impressive displacement seismogram from Hull Mountain, OR, ~350km NE of epicenterhttps://t.co/UjV0eGlscz pic.twitter.com/sA2zwYPskA— Anthony Lomax 🌍 (@ALomaxNet) January 25, 2018
Magnitude 5.8 #earthquake west of Cape Mendocino, N #California – southern transform boundary of Gorda micro-plate, most likely strike-slip motion (to be confirmed) pic.twitter.com/dXjxlyNAoP
— Robin Lacassin (@RLacassin) January 25, 2018
Mwp5.7 #earthquake
Off Coast of Northern California 2018.01.25-16:39:48https://t.co/UEHkvwYrXP pic.twitter.com/SnGJuDqrT3— Anthony Lomax 🌍 (@ALomaxNet) January 25, 2018
What today’s 5.8M looked like on our seismograph.
If you didn’t feel it, it may be because it was ~140 miles from campus. #HSUGeology #humboldtstate pic.twitter.com/oUGokFC3jB
— Humboldt State (@humboldtstate) January 25, 2018
- 1700.09.26 M 9.0 Cascadia’s 315th Anniversary 2015.01.26
- 1700.09.26 M 9.0 Cascadia’s 316th Anniversary 2016.01.26
- 1992.04.25 M 7.1 Cape Mendocino 25 year remembrance
- 1992.04.25 M 7.1 Cape Mendocino 25 Year Remembrance Event Page
- Earthquake Information about the CSZ 2015.10.08
- Gorda plate
- 2017.07.28 M 5.1 Gorda plate
- 2016.09.25 M 5.0 Gorda plate
- 2016.09.25 M 5.0 Gorda plate
- 2016.01.30 M 5.0 Gorda plate
- 2015.12.29 M 4.9 Gorda plate
- 2015.11.18 M 3.2 Gorda plate
- 2014.03.13 M 5.2 Gorda Rise
- 2014.03.09 M 6.8 Gorda plate p-1
- 2014.03.23 M 6.8 Gorda plate p-2
- Blanco fracture zone
- 2015.06.01 M 5.8 Blanco fracture zone p-1
- 2015.06.01 M 5.8 Blanco fracture zone p-2 (animations)
- Mendocino fault
- 2018.01.25 M 5.8 Mendocino fault
- 2017.09.22 M 5.7 Mendocino fault
- 2016.12.08 M 6.5 Mendocino fault, CA
- 2016.12.08 M 6.5 Mendocino fault, CA Update #1
- 2016.12.05 M 4.3 Petrolia CA
- 2016.10.27 M 4.1 Mendocino fault
- 2016.09.03 M 5.6 Mendocino
- 2016.01.02 M 4.5 Mendocino fault
- 2015.11.01 M 4.3 Mendocino fault
- 2015.01.28 M 5.7 Mendocino fault
- Mendocino triple junction
- 2017.03.06 M 4.0 Cape Mendocino
- North America plate
- 2016.11.02 M 3.6 Oregon
- 2016.01.07 M 4.2 NAP(?)
- 2015.10.29 M 3.4 Bayside
- Explorer plate
- 2017.01.07 M 5.7 Explorer plate
- 2016.03.19 M 5.2 Explorer plate
- Uncertain
- 2017.06.11 M 3.5 Gorda or NAP?
- 2016.07.21 M 4.7 Gorda or NAP? p-1
- 2016.07.21 M 4.7 Gorda or NAP? p-2
Cascadia subduction zone Earthquake Reports
General Overview
Earthquake Reports
- Atwater, B.F., Musumi-Rokkaku, S., Satake, K., Tsuju, Y., Eueda, K., and Yamaguchi, D.K., 2005. The Orphan Tsunami of 1700—Japanese Clues to a Parent Earthquake in North America, USGS Professional Paper 1707, USGS, Reston, VA, 144 pp.
- Chaytor, J.D., Goldfinger, C., Dziak, R.P., and Fox, C.G., 2004. Active deformation of the Gorda plate: Constraining deformation models with new geophysical data: Geology v. 32, p. 353-356.
- Dengler, L.A., Moley, K.M., McPherson, R.C., Pasyanos, M., Dewey, J.W., and Murray, M., 1995. The September 1, 1994 Mendocino Fault Earthquake, California Geology, Marc/April 1995, p. 43-53.
- Frisch, W., Meschede, M., Blakey, R., 2011. Plate Tectonics, Springer-Verlag, London, 213 pp.
- Geist, E.L. and Andrews D.J., 2000. Slip rates on San Francisco Bay area faults from anelastic deformation of the continental lithosphere, Journal of Geophysical Research, v. 105, no. B11, p. 25,543-25,552.
- Irwin, W.P., 1990. Quaternary deformation, in Wallace, R.E. (ed.), 1990, The San Andreas Fault system, California: U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1515, online at: http://pubs.usgs.gov/pp/1990/1515/
- McCrory, P.A.,. Blair, J.L., Waldhauser, F., kand Oppenheimer, D.H., 2012. Juan de Fuca slab geometry and its relation to Wadati-Benioff zone seismicity in JGR, v. 117, B09306, doi:10.1029/2012JB009407.
- McLaughlin, R.J., Sarna-Wojcicki, A.M., Wagner, D.L., Fleck, R.J., Langenheim, V.E., Jachens, R.C., Clahan, K., and Allen, J.R., 2012. Evolution of the Rodgers Creek–Maacama right-lateral fault system and associated basins east of the northward-migrating Mendocino Triple Junction, northern California in Geosphere, v. 8, no. 2., p. 342-373.
- Nelson, A.R., Asquith, A.C., and Grant, W.C., 2004. Great Earthquakes and Tsunamis of the Past 2000 Years at the Salmon River Estuary, Central Oregon Coast, USA: Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 94, No. 4, pp. 1276–1292
- Rollins, J.C. and Stein, R.S., 2010. Coulomb stress interactions among M ≥ 5.9 earthquakes in the Gorda deformation zone and on the Mendocino Fault Zone, Cascadia subduction zone, and northern San Andreas Fault: Journal of Geophysical Research, v. 115, B12306, doi:10.1029/2009JB007117, 2010.
- Stoffer, P.W., 2006, Where’s the San Andreas Fault? A guidebook to tracing the fault on public lands in the San Francisco Bay region: U.S. Geological Survey General Interest Publication 16, 123 p., online at http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/2006/16/
- Wallace, Robert E., ed., 1990, The San Andreas fault system, California: U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1515, 283 p. [http://pubs.usgs.gov/pp/1988/1434/].